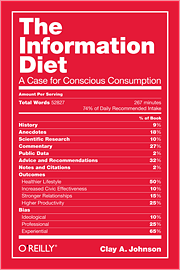
We all know a diet of fast food can cause obesity, but can consuming junk information damage our mental fitness and critical faculties?
In The Information Diet, Clay A. Johnson builds the case for being more selective in what we read, watch and listen to. In it, Clay describes how we have reached the stage of intellectual obesity, what constitutes a poor diet and suggests strategies to improve the quality of the information we consume.
The Information Diet is based upon a simple premise, that just as balanced food diet is important for physical health so too is a diverse intake of news and information necessary for a healthy understanding of the world.
Clay A. Johnson came to this view after seeing a protestor holding up a placard reading “Keep your government hands off my Medicare.” Could an unbalanced information diet cause a kind of intellectual obesity that warps otherwise intelligent peoples’ perspectives?
The analogy is well explored by Clay as he looks at how we can go about creating a form of “infoveganism” that favours selecting information that comes as close from the source as possible
Just as fast food replaces fibre and nutrients with fat, sugars and salt to appeal to our tastes, media organisations process information to appeal to our own perceived biases and beliefs.
Clay doesn’t just accuse the right wing of politics in this – he is as scathing of those who consider the DailyKos, Huffington Post or Keith Olbermann as their primary sources as those who do likewise with Fox News or Bill O’Reilly.
The rise of opinion driven media – something that pre-dates the web – has been because the industrial production of processed information is quicker and more profitable that the higher cost, slower alternatives; which is the same reason for the rise of the fast food industry.
For society, this has meant our political discourse has become flabbier as voters base decisions and opinions upon information that has had the facts and reality processed out of it in an attempt to attract eyeballs and paying advertisers.
In many ways, Clay has identified the fundamental problem facing mass media today; as the advertising driven model requires viewers’ and readers’ attention, producers and editors are forced to become more sensationalist and selective. This in turn is damaging the credibility of these outlets.
Unspoken in Clay’s book is the challenge for traditional media –their processing of information has long since stopped adding value and now strips out the useful data, at best dumbing down the news into a “he said, she said” argument and at worse deliberately distorting events to attract an audience.
While traditional media is suffering from its own “filter failure”, the new media information empires of Google, Facebook, Apple and Amazon are developing even stronger feedback loops as our own friends on social media filter the news rather than a newsroom editor or producer.
As our primary sources of information have become more filtered and processed, societal and political structures have themselves become flabby and obese. Clay describes how the skills required to be elected in such a system almost certainly exclude those best suited to lead a diverse democracy and economy.
Clay’s strategies for improving the quality of the information we consume are basic, obvious and clever. The book is a valuable look at how we can equip ourselves to deal with the flood of data we call have to deal with every day.
Probably the most important message from The Information Diet is that we need to identify our biases, challenge our beliefs and look outside the boxes we’ve chosen for ourselves. Doing that will help us deal with the opportunities of the 21st Century.
Clay A. Johnson’s The Information Diet is published by O’Reilly. A complimentary copy was provided as part of the publisher’s blogger review program.