Last year the Committee for Economic Development, Australia (CEDA) warned over 40% of the nation’s jobs were at risk from automation over the next 15 years.
While that focus was on the risks to workers, it’s equally threatening for small business. Many companies and sole traders are facing the same disruptions from technological change.
This isn’t a new phenomenon, in the Twentieth century the motor car displaced thousands of small businesses that catered to the horse drawn economy and family run corner stores were displaced by the arrival of supermarkets in the 1950s.
Beyond the personal computer era
At the end of the last century the personal computer’s arrival revolutionised small businesses as suddenly tools that were previously only in the reach of big organisations were suddenly accessible to the most modest venture.
One of the early beneficiaries of that shift to desktop computers in 1990s was the bookkeeping industry which took off as a legion of home based contractors catered for local small businesses.
As the internet and smartphones came along, the bookkeeping market changed as features like bank feeds and receipt apps automated many previously manual tasks.
Despite those challenges the bookkeeping industry has survived and continues to grow with IBIS World estimating the overall accounting industry, which includes bookkeepers, grew 2.6% per year over the past five years.
Close to customers
The success of bookkeepers and accountants in navigating change is probably due to industry being close to their clients along with being early adopters of new technology, two things that caught the taxi industry out when Uber arrived.
Uber’s success in upturning the taxi industry illustrates just how important understanding emerging technologies is for smaller businesses. One industry currently facing massive disruption from robots is the construction sector.
The trades were thought to be relatively immune from automation – after all, who’s going to build a robot plumber? But now robots are moving into trades like bricklaying, as Australian startup Fastbrick Robotics shows.
Fastbrick are building a commercial bricklaying machine, Hadrian X, that automates the trade’s physical work and integrates with 3D printing technology.
In one respect the robot bricklayers are bad for the trade’s employment prospects but for older brickies with bad backs having a machine to help you is a godsend while for employers it improves productivity and reduces workplace accidents. It won’t be the end of the trade but the contractors who survive will have adapted to a very different construction industry.
Restructuring industries
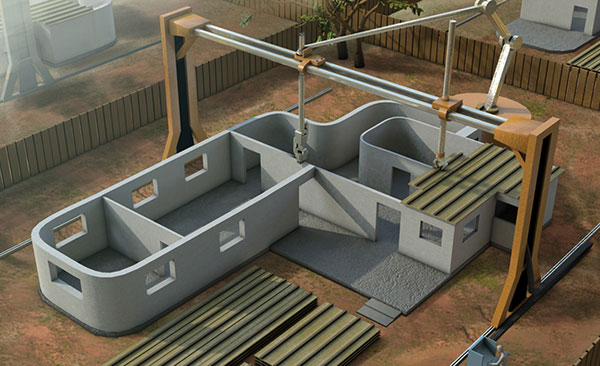
That Fastbrick integrates with design software shows how the dynamics of the construction are changing. In 2014 Chinese company Winsun demonstrated how they can build ten houses in a day with large scale 3D printers.
While we may not see that particular technology in Australia, aspects of it will be used and they are going to change all the trades and professions related to the building industry.
Architects are one building industry group that have long dealt with technological change. Like bookkeepers, the arrival of personal computers completely changed their profession and those who adapted thrived.
Now with cloud computing services plugging into builders’ supply chains like Winsun and machines like Fastbrick’s, architects are closer than ever to the worksite and their customers. The ones who are adapting are the earlier adopters who are getting into these technologies further.
Disrupting the professions
Accountants and architects aren’t the only professions being affected, lawyers are facing a new wave of services using artificial intelligence to do many legal tasks ranging from a chatbot that appeals traffic fines to a program that predicts US Supreme Court decisions.
Like other sectors, it’s the early adopters in the legal sector who are adapting to a very different industry with much of the manual, lower level work being automated out.
The wave of technology we’re now seeing appear – including robots, autonomous vehicles, machine learning and artificial intelligence – are going to change our industries and workplaces dramatically in the next few years.
What the accounting industry and the architecture profession teach us is the businesses closest to their customers and those adopting technology early will be the ones who thrive in a very different industries. Researching, experimenting and paying attention will be the keys to business survival.
An open mindset
Even for the trades, survival during this wave of technological change will be a matter of watching the marketplace closely while being open to new methods and technologies.
Assuming it won’t happen to your industry is probably one of the riskiest things of all. Ten years ago the idea of smartphones revolutionising the taxi business or that robots could replace bricklayers was unthinkable. Now it’s almost expected.
The forces that are changing the workplace are also changing industries and markets, so small businesses will also be affected. It’s going to pay to be smart and curious.